What is Streaming Video and Streaming Media?
Streaming video is a sequence of “moving images” that are sent in compressed form over the Internet and displayed by the viewer as they arrive. Streaming media is streaming video with sound. Streaming multimedia allows the user to begin viewing videos without first downloading the entire file. After a brief period of initializing and buffering, the file will begin to stream – or play – in real-time.
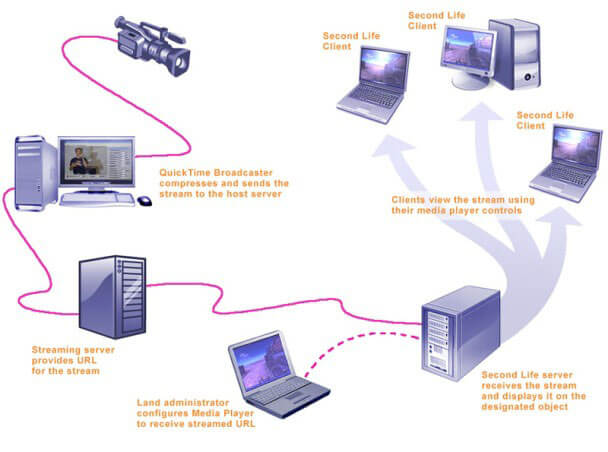
In a live broadcast, the video signal is converted into a compressed digital signal and transmitted from a special Web server that is able to do multicast, sending the same file to multiple users at the same time.
Your picture quality will be determined by your available bandwidth (download speed) and computer processor speed. Users with older processors and slower modem connections will have more dropped frames and pixelization. The streaming video will be limited to the data rates of the connection (for example, up to 128 Kbps with an ISDN connection).
The user needs a player, which is a special program that uncompresses and sends video data to the display and audio data to the speakers. A player can be either an integral part of a browser or downloaded from the software maker’s Web site. Examples of streaming video and audio include Internet radio and television broadcasts, and corporate webcasts.
