What is the difference between PCMCIA and ExpressCard?
New laptops do not include PCMCIA ports but do include ExpressCard ports. There are two Express Card formats – 54 and 34....
New laptops do not include PCMCIA ports but do include ExpressCard ports. There are two Express Card formats – 54 and 34....
The Expresscard module comes in two sizes. Expresscard/34 is 34 mm wide, while Expresscard/54 is 54 mm wide. The modules are both 5 mm high and 75 mm long. The 34 mm module has the advantage in that it can fit into the slot designed for the 54 mm card, but not vice versa....
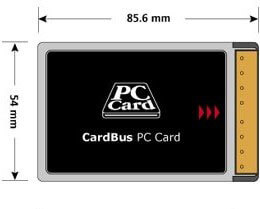
CardBus is the latest enhancement to the PCMCIA 5.0 or later. PMCIA stands for Personal Computer Memory Card International Association. CardBus was introduced in 1995 and has been present in laptops from late 1997 onward. The main purpose of CardBus was to extend the existing PCMCIA bus to allow more powerful devices and provide support for 32 Bit I/O. CardBus includes bus mastering, which allows a controller on the bus to talk to other devices or memory without going through the CPU. CardBus also can operate at speeds up to 33MHz....

PCMCIA is short for Personal Computer Memory Card International Association. It is pronounced as separate letters. PCMCIA is also known as PC Card....
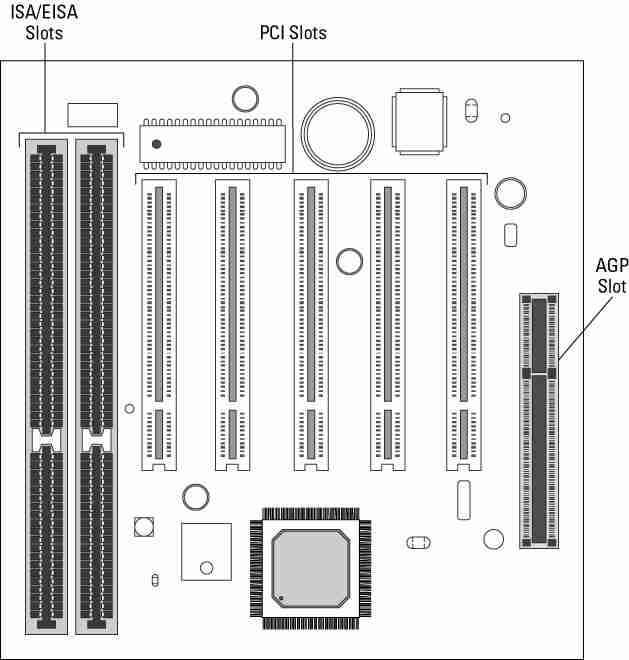
The primary advantage of AGP over PCI is that it provides a dedicated pathway between the slot and the processor rather than sharing the PCI bus. In addition to a lack of contention for the bus, the point-to-point connection allows for higher clock speeds.
AGP also uses sideband addressing, meaning that the address and data buses are separated so the entire packet does not need to be read to get addressing information. This is done by adding eight extra bits which allow the graphics controller to issue new AGP requests and commands at the same time with other AGP data flowing via the main 32 address/data (AD) lines. This results in improved overall AGP data throughput....
PCI-Express, on the other hand, uses a serial interconnect along a switched bus dedicated exclusively to that slot. PCI-Express has the unique capability of multiplying up individual data lanes, to produce aggregate interconnects that can deliver up to 16 times the bandwidth of a single lane....
PCI Express stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect Express. It is also known as PCIe. PCI Express expands on and doubles the data transfer rates of the original PCI. PCI Express is a two-way, serial connection that carries data in packets along two pairs of point-to-point data lanes.
PCIe was developed in 2004, it was designed to provide higher performance and bandwidth than PCI or AGP. While some standard PCI slots can still be found on motherboards, many computer users prefer PCI express for graphics cards....
AGP Pro was launched in 1998 as an AGP interface extension specification for advanced workstations. AGP Pro bus is a specification that provides a direct connection between the graphics adapter and memory. It has a larger slot, with more voltage pins for high-consumption 3D video cards. The AGP Pro is compatible with the previous versions of the AGP bus.
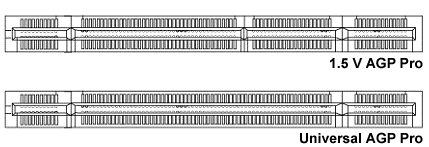
AGP Pro delivers additional power to video cards and includes an extended connector, thermal envelope, updated mechanical specifications, and I/O bracket....
AGP is commonly used for games that require the image displayed on the monitor is calculated from a data stream, rather than simply passed through the computer like a television signal....
PCI-X has been replaced in modern designs by the similar-sounding PCI Express, with a completely different connector and a quite different logical design....
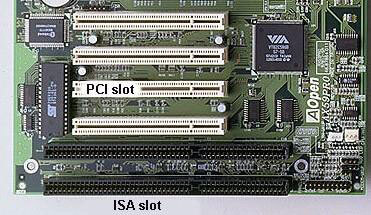 ...
...
PCI has evolved into several variations (PCI, PCI-X, PCMCIA, CardBus, CompactPCI, etc.), all parallel bus technologies, to meet the specific requirements of its many applications....
ISA stands for Industry Standard Architecture. ISA was introduced in 1981 as a type of bus used in PCs for adding expansion cards. ISA is one of the oldest forms of an expansion slot on a computer’s motherboard. ISA original 8-bit version.
In 1993, Intel and Microsoft introduced the latest version of the ISA specification called Plug and Play ISA. Plug and Play ISA enables the operating system to configure expansion boards automatically so that users do not need to fiddle with DIP switches and jumpers....
 ...
...

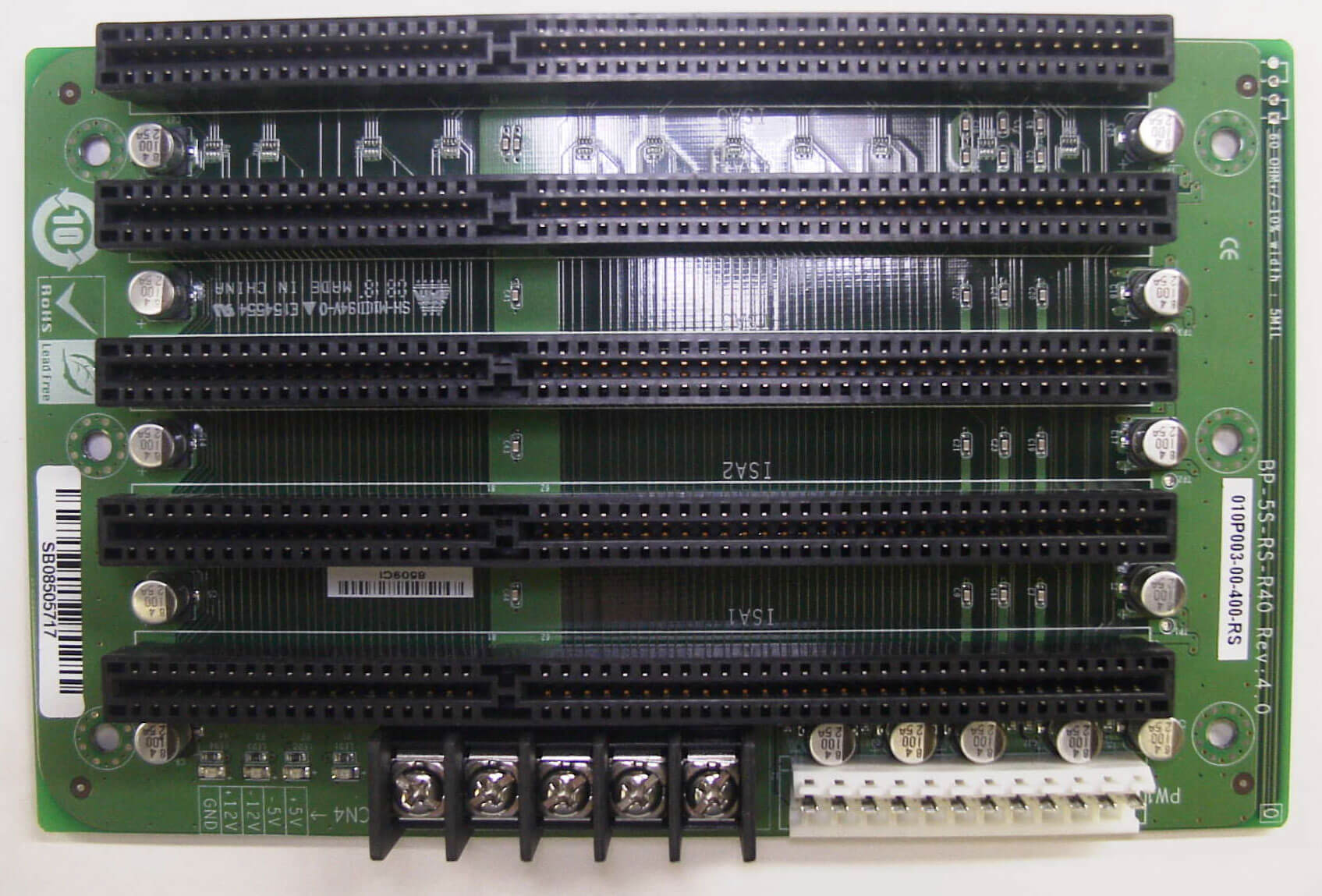
An expansion board is a printed circuit board that you can insert into a computer to give it added capabilities, such as by increasing memory or improving graphics. Expansion boards are also called adapters, cards, add-ins, and add-ons.
Below there are two examples of expansion boards, one for I/O components and the other for memory expansion....